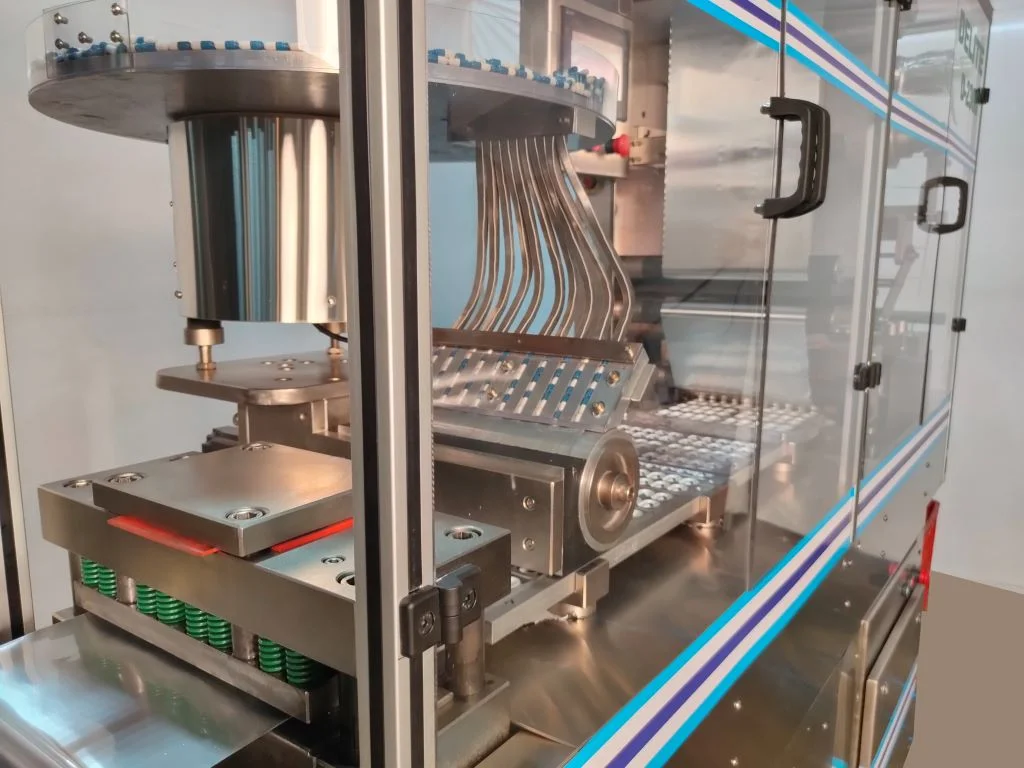
Features of Fluid bed dryer
- Fully automatic operation based on PLC control. (optional)
- Minimum handling and more hygienic.
- Top Mounted telescopic cylinder for auto bag shaking. (optional)
- Clamp type bottom mesh for container.
- Capacity available from 2.5 kgs. to 300 kgs.
- MOC SS 304 / 316 / 316L
- cGMP with documentation.
- Very versatile
Fluid bed dryer to minimize moisture from ingredients used by pharma companies
Fluid bed dryer is used by pharma companies to minimize moisture from materials such as granules, powders, fertilizers, and further also materials like plastics. As a result Pharmaceutical, Chemical, Food, Dyes, and other such process industries use them. They adopt the principle of fluidization and hence it got its name. Fluidization converts material from a static solid-like state to a dynamic fluid-like state so as to facilitate drying. A perforated plate likewise introduces hot air into the area holding the material.
The Working Principle
The hot air thus pumps through the spaces between solid particles. The increased velocity of the air thereby increases, and hence the upward forces on the particles increase. This further causes them to equal the gravitational forces below. This thus creates a state of fluidization. This state hence suspends the particles in what appears to be a boiling bed of liquid. Therefore what once moved in a solid way can now flow like water. Hot air surrounds each particle, thus creating an efficient and uniform drying process.
Technical specifications of fluid bed dryer
| Model | DFBD15 | DFBD30 | DFBD60 | DFBD120 | DFBD200 | DFBD300 |
| Container Gross Volume Liters. | 46 | 71 | 142 | 280 | 475 | 650 |
| Maximum Batch Capacity (0.5bd) Kg | 10 to 15 | 20-30 | 40-60 | 80-120 | 160-200 | 200-300 |
| Blower motor Hp | 5 | 7.5 | 10 | 20 | 25 | 30 |
| Air Flow (CFM) ¡¾ 10% | 430 | 706 | 1060 | 1880 | 2590 | 3235 |
| Steam Consumption (kg /hour) | 30 | 50 | 80 | 140 | 216 | 215 |
| Electric Heater (KW) | 20 | 20 | 36 | 60 | NA | NA |
| Steam Pressure (kg / cm2) | 3.5 | |||||
| Compressed Air Pressure (bar) | 6 | |||||
| Drying temp (¢ªC) | 35 to 80 | |||||
| Power Supply | 415 V, ¡¾ 10%, 3 Phase, AC |
Guide to choosing good quality fluid bed dryer by pharma companies
- The equipment should heat, cool, and furthermore, do the coating. Thus it should be a multi-tasker.
- it should transfer heat with minimal energy and hence it should be energy efficient.
- Furthermore, it should Adapt to continuous or batch processing.
- It should have proper vibration so as to aid the process.
- It should be GMP compliant and hence made out of stainless steel 316.
- Fluid bed dryer should run with high efficiency and hence should have negligible maintenance
Importance of fluid bed dryer to pharma companies
While it’s true that a variety of industries use it however it has its greatest impact on pharma companies. A fluid bed dryer reduces the moisture content of granules/powder and further, it does it consistently. This technology has hence replaced the traditional method of drying products in trays. The system controls the inlet air temperature therefore the correct amount of moisture evaporates from the surface of the granule. High temperature causes surface crust, thus not allowing deeper moisture to come to the surface. This phenomenon can delay the drying process rather than accelerate it.
Other machines for pharma companies